Nutrition and Diet Advice for Older Adults
Expert guidance on balanced diets, hydration, and special nutritional needs for seniors to maintain health and vitality.
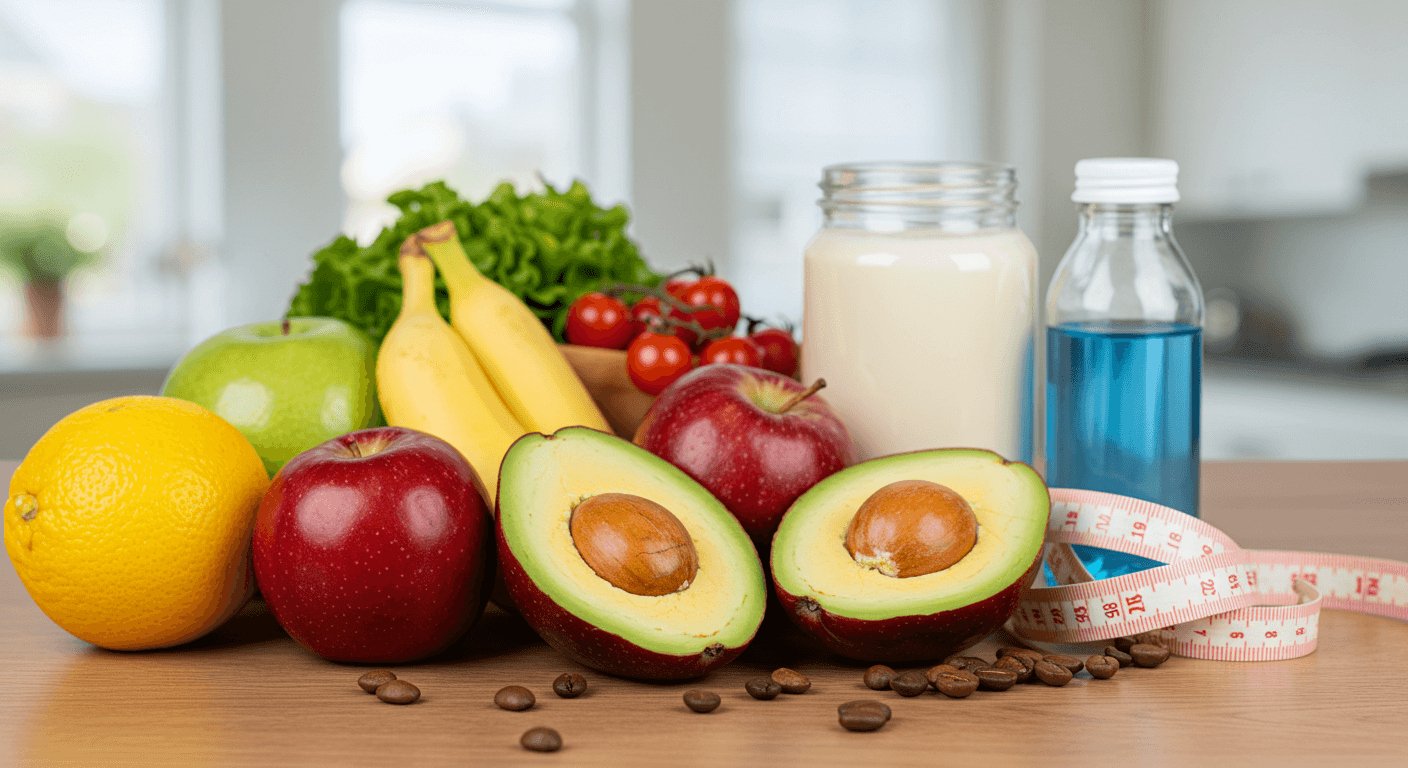

Proper nutrition is crucial for seniors to maintain energy, manage chronic conditions, and support overall well-being. This guide provides practical advice for caregivers.
1. Assess Dietary Needs
Consult with a healthcare provider to understand specific nutritional requirements based on health conditions, medications, and activity level.
2. Plan Balanced Meals
Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and dairy to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
3. Ensure Proper Hydration
Encourage regular fluid intake throughout the day, as seniors are at higher risk of dehydration. Offer water, herbal teas, and hydrating foods.
4. Adapt for Chewing or Swallowing Issues
Modify textures if needed—soft foods, purees, or nutrient-dense shakes can help those with dental problems or dysphagia.
5. Monitor and Adjust
Regularly review dietary habits and weight, adjusting portions or foods as needed to address changes in appetite or health status.
The Science Behind Senior Nutrition
Aging affects metabolism, nutrient absorption, and appetite. Adequate protein prevents muscle loss, calcium and vitamin D support bone health, and fiber aids digestion.
Emergency guidance
Signs of Malnutrition
Watch for unexplained weight loss, fatigue, weakness, or poor wound healing. Seek medical advice promptly if these occur.
Dehydration Warning Signs
Dry mouth, dark urine, dizziness, or confusion require immediate attention. Encourage fluids and consult a doctor if severe.
Pro tips
- Incorporate favorite foods to improve appetite and enjoyment.
- Use herbs and spices instead of salt to enhance flavor without increasing sodium.
Common pitfalls
Neglecting nutritional needs can lead to weakened immunity, increased fall risk, and slower recovery from illness.
Recommended reads

You may also like






